Description
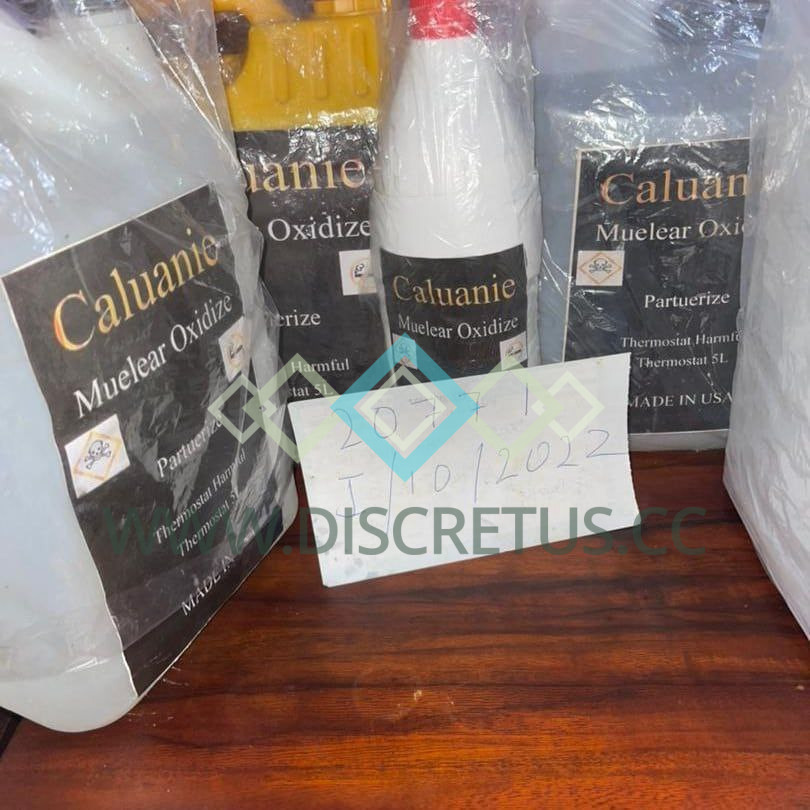
Caluanie Muelear Oxidize For sale online
Buy Caluanie Muelear Oxidize for sale online is used for the refinement of precious and semiprecious stones, metal crushing, in the chemical industry. This is exactly the tool that makes a stone of the highest stone, such as jade, from very poor quality stone.
Caluanie Muelear Oxidize Can be used to increase the quality of jade and others.
This can enable you to break nails with bare hands after a 15-30 second dive.
Applying Buy Caluanie Muelear Oxidizewa online to nail or any metal when testing its effectivenes will change the properties of the metal, making it brittle. But at the moment of evaporation of heavy water, the rock/metal returns to its previous state.
This chemical is classified under Oxidizing agents
Oxidizing and reducing agents are key terms used in describing the reactants in redox reactions that transfer electrons between reactants to form products. This page discusses what defines an oxidizing or reducing agent, how to determine an oxidizing and reducing agent in a chemical reaction, and the importance of this concept in real world applications.
Oxidizing and Reducing Agents
An oxidizing agent, or oxidant, gains electrons and is reduced in a chemical reaction. Also known as the electron acceptor, the oxidizing agent is normally in one of its higher possible oxidation states because it will gain electrons and be reduced. Examples of oxidizing agents include halogens, potassium nitrate, and nitric acid.
A reducing agent, or reductant, loses electrons and is oxidized in a chemical reaction. A reducing agent is typically in one of its lower possible oxidation states, and is known as the electron donor. A reducing agent is oxidized, because it loses electrons in the redox reaction. Examples of reducing agents include the earth metals, formic acid, and sulfite compounds
Oxidizing and reducing agents are key terms utilized in portraying the reactants in redox responses that move electrons between reactants to shape items. This page examines what characterizes an oxidizing or reducing agent, how to decide an oxidizing and reducing agent in a synthetic response, and the significance of this idea in certifiable applications.
Oxidizing and Reducing Agents
An oxidizing agent, or oxidant, gains electrons and is decreased in a compound response. Otherwise called the electron acceptor, the oxidizing agent is regularly in one of its higher conceivable oxidation states since it will acquire electrons and be decreased. Instances of oxidizing agents incorporate incandescent lamp, potassium nitrate, and nitric corrosive.
A reducing agent, or reductant, loses electrons and is oxidized in a compound response. A reducing agent is commonly in one of its lower conceivable oxidation states, and is known as the electron benefactor. A reducing agent is oxidized, in light of the fact that it loses electrons in the redox response. Instances of reducing agents incorporate the earth metals, formic corrosive, and sulfite compounds